With the Covid19 pandemic and lockdown measures keeping the population at home from 17th March to 11th May, people and companies made massive use of digital and internet solutions. However the health crisis revealed great disparities in the conditions of access to digital technology.

Uses of digitisation need a constantly increasing amount of digital flow in all fields of human activity: various and simultaneous use in the home, new modes of work and new professional practices with widespread use of digital supports and new services. This ever growing consumption of digitisation, particularly when people are on the move, is a prevailing trend and can be expected to increase with the arrival of the 5G and the development of object to object connection.
During the health crisis, under lockdown, the use of digitisation exploded particularly in homes and certain e-health, e-education and telework applications which increased significantly. Digital technology also facilitated the implementation of solidarity actions.
Digital practices have one point in common; they require access to internet through an electronic telecommunication network and consume a lot of digital broadband. In this context, optical fibre appears as the leading technological solution for high speed access to internet, be it end to end or a technological mix.
On a regional and national scale, the Metropole du Grand Paris (MGP) appears privileged in its ease of access to internet particularly via optical fibre. However, certain territories are still lagging behind in the deployment of infrastructures.
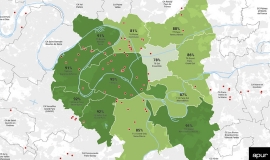
This note describes a particular aspect of access to digitisation in Métropole du Grand Paris: the possibility of being connected to the public optical fibre network by taking out a subscription for fixed-line, very high-speed internet. It presents the main results of the urban approach developed by Apur in 2019 of closely monitoring the progress of deployment in specific sectors which have urban or social issues, such as areas of detached housing, urban cohesion policy neighbourhoods and areas where Local Urbanism Plans are underway. The indicators presented, which were recorded at the end of 2018 using data made available on Open Data by the Electronic Communications and Postal Regulatory Authority - l’Autorité de régulation des communications électroniques et des postes -, call for certain bodies to be rigorous and will be updated at the end of 2020.